POS software, or Point of Sale software, is way more than just a cash register these days. It’s the backbone of efficient operations for countless businesses, from bustling coffee shops to sprawling retail giants. Think of it as your digital command center, streamlining everything from sales tracking and inventory management to customer relationship building and insightful data analysis. We’re diving deep into the world of POS systems, exploring everything you need to know to choose, implement, and maximize the power of this essential business tool.
This guide will cover the core functionalities of POS systems, helping you understand the differences between cloud-based and on-premise solutions. We’ll also walk you through selecting the right software for your needs, including crucial factors like integration capabilities, security features, and scalability. Get ready to learn how to unlock the full potential of POS software and propel your business to new heights!
POS Software Features
Okay, so you’re thinking about getting a POS system for your business, right? Smart move! A good POS system can be a total game-changer, streamlining operations and boosting your bottom line. Let’s dive into the key features you should be looking for.
At its core, a POS system is designed to manage sales transactions efficiently. This includes everything from ringing up customers and processing payments to tracking inventory and generating reports. But the specific features can vary wildly depending on your needs and the type of system you choose.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise POS Systems
Cloud-based POS systems store data on remote servers, accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. This offers flexibility and scalability, allowing you to access your data from multiple locations and easily add new features as needed. On-premise systems, however, store data on your own servers, offering greater control over your data but requiring more upfront investment and ongoing maintenance.
Think of it like this: cloud-based is like renting an apartment – easy setup, flexible, and you don’t worry about repairs. On-premise is like owning a house – more control, but you’re responsible for everything.
Inventory Management Features
Effective inventory management is crucial for any business. A robust POS system should offer features like real-time inventory tracking, low-stock alerts, and the ability to manage multiple locations. Imagine this: you’re a small bakery and your POS system alerts you that you’re running low on flour. You can immediately order more, avoiding lost sales and unhappy customers. These features help optimize stock levels, reduce waste, and ensure you always have what you need to meet customer demand.
Integrated Payment Processing
Integrating payment processing directly into your POS system simplifies transactions and reduces errors. This means customers can pay with credit cards, debit cards, mobile wallets, and other digital payment methods seamlessly. The benefits are clear: faster checkout times, reduced manual data entry, and improved security. Plus, you get detailed sales reports that include payment method breakdowns, providing valuable insights into customer preferences and payment trends.
For example, if you see a significant increase in mobile wallet payments, you can adjust your marketing strategy to emphasize those options.
POS Software Selection Criteria

Picking the right POS system is like choosing the perfect pair of shoes – you need something that fits your business perfectly, is comfortable to use, and will last the long haul. A poorly chosen system can lead to headaches, lost sales, and ultimately, a frustrated team. So, let’s break down how to make the right choice.Choosing the right POS system involves careful consideration of several key factors.
These factors go beyond just the initial price tag and delve into the long-term impact on efficiency, customer experience, and overall business growth. A thorough evaluation ensures a smooth integration and maximizes the return on investment.
Key Factors for POS Software Selection
Businesses should prioritize several crucial aspects when evaluating POS software. These considerations encompass functionality, scalability, cost, and integration capabilities. Ignoring these elements can result in a system that doesn’t meet the business’s needs or creates more problems than it solves.
- Functionality: Does the system handle all necessary transactions (sales, returns, payments)? Does it offer inventory management, employee management, reporting, and customer relationship management (CRM) features? Consider specific needs like loyalty programs or online ordering integration.
- Scalability: Can the system adapt to future growth? Will it handle an increase in transactions, inventory, or employees without significant performance issues or requiring costly upgrades?
- Cost: This includes the initial purchase price, monthly subscription fees, transaction fees, and any additional costs for hardware, software updates, or support. Consider the total cost of ownership over several years.
- Integration: Does the POS system integrate with other essential business software, such as accounting software, e-commerce platforms, or CRM systems? Seamless integration streamlines operations and minimizes data entry.
- Ease of Use: The system should be intuitive and easy for employees to learn and use. A complicated system can lead to errors and decreased efficiency.
- Hardware Compatibility: Ensure compatibility with existing hardware (printers, barcode scanners, credit card readers) or the willingness to invest in new hardware.
- Customer Support: Reliable customer support is crucial. Look for vendors offering responsive technical support, training, and documentation.
Decision-Making Matrix for POS System Comparison
A decision matrix provides a structured approach to comparing different POS systems. This allows for a side-by-side comparison of key features and helps visualize the strengths and weaknesses of each option.
| Feature | System A | System B | System C | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price | $50/month | $75/month | $100/month | 3 |
| Inventory Management | Excellent | Good | Fair | 5 |
| Reporting Capabilities | Good | Excellent | Poor | 4 |
| Customer Support | Good | Fair | Excellent | 2 |
| Ease of Use | Excellent | Good | Poor | 5 |
Each feature is assigned a weight reflecting its importance to the business. For example, a business prioritizing inventory management might assign a higher weight to that feature. Each system is then rated on a scale (e.g., Excellent, Good, Fair, Poor) and a weighted score is calculated for each system. The system with the highest weighted score is the most suitable option.
Essential Questions for POS Software Vendors
Asking the right questions to potential vendors is critical for gathering essential information. These questions ensure a clear understanding of the system’s capabilities, limitations, and the vendor’s support structure. Don’t be shy – this is your investment.
- What are the system’s key features and limitations?
- What types of hardware are compatible?
- What is the pricing structure (including setup fees, monthly fees, transaction fees)?
- What level of customer support is provided?
- What is the vendor’s reputation and track record?
- What is the process for software updates and maintenance?
- What security measures are in place to protect customer data?
Evaluating POS Software Demos
A demo is your chance to see the software in action and assess its usability. A well-structured evaluation ensures you’re making an informed decision based on practical experience.
- Test Key Features: During the demo, actively test the features most important to your business. Process simulated transactions, explore reporting capabilities, and assess the ease of use.
- Assess User Interface: Is the interface intuitive and easy to navigate? Can employees easily understand and use the system?
- Check for Bugs and Errors: Look for any glitches, errors, or unexpected behavior during the demo. This indicates potential problems with the software’s stability.
- Evaluate Reporting Capabilities: Examine the types of reports the system generates. Are they comprehensive, easy to understand, and relevant to your business needs?
- Ask Clarifying Questions: Don’t hesitate to ask questions about any aspects of the software that are unclear or require further explanation.
POS Software Implementation
Implementing new POS software can feel like a massive undertaking, but with careful planning and execution, it can be a smooth transition that boosts efficiency and profitability. A successful implementation hinges on thorough preparation, effective training, and ongoing monitoring. Let’s break down the key elements to ensure your POS system upgrade is a win.
Best Practices for Smooth POS Software Implementation
A well-defined implementation plan is crucial. This should include setting realistic timelines, assigning roles and responsibilities to team members, and establishing clear communication channels. Prioritize thorough testing of the new system in a sandbox environment before going live. This allows you to identify and resolve any bugs or glitches before they impact your daily operations. Regular communication with the software vendor is also key – they’re your partner in this process and can provide invaluable support.
Finally, consider a phased rollout, starting with a smaller section of your business, to minimize disruption and allow for adjustments based on early feedback.
The Importance of Employee Training in Successful POS Adoption
Effective employee training is the cornerstone of successful POS adoption. Employees need comprehensive training on all aspects of the new system, from basic navigation to advanced features. Hands-on training sessions, coupled with readily available documentation and ongoing support, ensure staff feel comfortable and confident using the new system. Ignoring this step can lead to errors, slowdowns, and ultimately, frustration among your team.
Think of it as an investment – well-trained employees are more efficient, make fewer mistakes, and contribute to a smoother transition overall. For example, a restaurant chain might dedicate a week to training all staff on the new system, using a combination of online modules, group sessions, and individual practice time.
Migrating Data from an Old System to a New POS
Data migration is a critical step that requires careful planning and execution. Begin by thoroughly assessing the data you need to migrate, ensuring data quality and accuracy. Develop a detailed migration plan, including data cleansing, transformation, and validation procedures. Utilize the software vendor’s recommended migration tools and techniques to minimize errors and ensure data integrity. Consider employing a third-party data migration specialist for large or complex datasets to minimize risks and ensure a smooth transition.
For instance, a retail store with years of sales data might hire a specialist to migrate the data while ensuring that all historical sales records are accurately transferred to the new system. Testing the migrated data in the new system is essential to verify its accuracy and completeness.
Post-Implementation Monitoring and Support Checklist
Post-implementation monitoring is essential to identify and address any unforeseen issues. This should include regular system checks, performance monitoring, and user feedback collection. Establish a help desk or support system to address user queries and technical issues promptly. Conduct regular training refresher sessions to ensure staff stay up-to-date with the system’s features and functionalities. Review key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess the system’s impact on efficiency and profitability.
A checklist might include: daily system checks, weekly performance reviews, monthly user feedback surveys, and quarterly system updates. This proactive approach ensures ongoing optimization and prevents potential problems from escalating.
POS Software Integrations
Integrating your point-of-sale (POS) system with other business tools is like adding turbochargers to your engine – it significantly boosts efficiency and unlocks a wealth of data-driven insights. By connecting your POS to applications like accounting software, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and inventory management tools, you create a streamlined workflow that minimizes manual data entry, reduces errors, and provides a holistic view of your business performance.This interconnectedness allows for automated processes, improved decision-making, and ultimately, a more profitable operation.
Think of it as creating a central nervous system for your business, where information flows seamlessly between different departments and functions.
API Integration Methods
Different POS systems offer varying API (Application Programming Interface) integration methods, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right method depends on factors such as your technical expertise, the complexity of the integration, and the specific needs of your business. Common methods include RESTful APIs, SOAP APIs, and proprietary APIs. RESTful APIs are generally preferred for their simplicity, scalability, and widespread adoption.
They use standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) to interact with data, making them relatively easy to understand and implement. SOAP APIs, on the other hand, are more complex and often require specialized tools and expertise. Proprietary APIs are specific to a particular POS system and may limit your flexibility in choosing other business tools.
Examples of Successful POS Software Integrations and Their Impact
A successful example is a restaurant integrating its POS with a reservation system. This integration allows the restaurant to automatically update table availability in real-time, reducing double-bookings and improving customer satisfaction. The data collected from both systems can then be used for detailed sales analysis and forecasting. Another example involves a retail store integrating its POS with an e-commerce platform.
This enables seamless inventory management, allowing the store to accurately track stock levels across both online and offline channels, preventing stockouts and optimizing inventory costs. This integration also allows for consistent pricing and order fulfillment across platforms. In both instances, the integration significantly improved operational efficiency and provided valuable insights into sales trends and customer behavior, directly impacting profitability and customer experience.
Security Considerations for POS Software Integrations
Security is paramount when integrating your POS system with third-party applications. Data breaches can have devastating consequences, impacting your financial health and damaging your reputation. Therefore, it’s crucial to choose POS systems and third-party applications with robust security features. This includes using secure APIs (HTTPS), implementing strong authentication and authorization mechanisms, and regularly updating software to patch security vulnerabilities.
Consider encrypting sensitive data both in transit and at rest, and conduct regular security audits to identify and address potential weaknesses. Adopting a zero-trust security model, where every user and device is verified before access is granted, is a best practice for enhanced protection. Regularly reviewing and updating your integration protocols is also critical to adapt to evolving security threats.
So, you’re looking at POS software? Choosing the right system is key for smooth operations. Often, you’ll need robust data management, which is where integrating tools like those found in the microsoft office suite can really boost efficiency. Think Excel for inventory, Word for reports – it all ties into your overall POS strategy. Ultimately, a good POS system needs to work seamlessly with your other software.
POS Software Cost and ROI
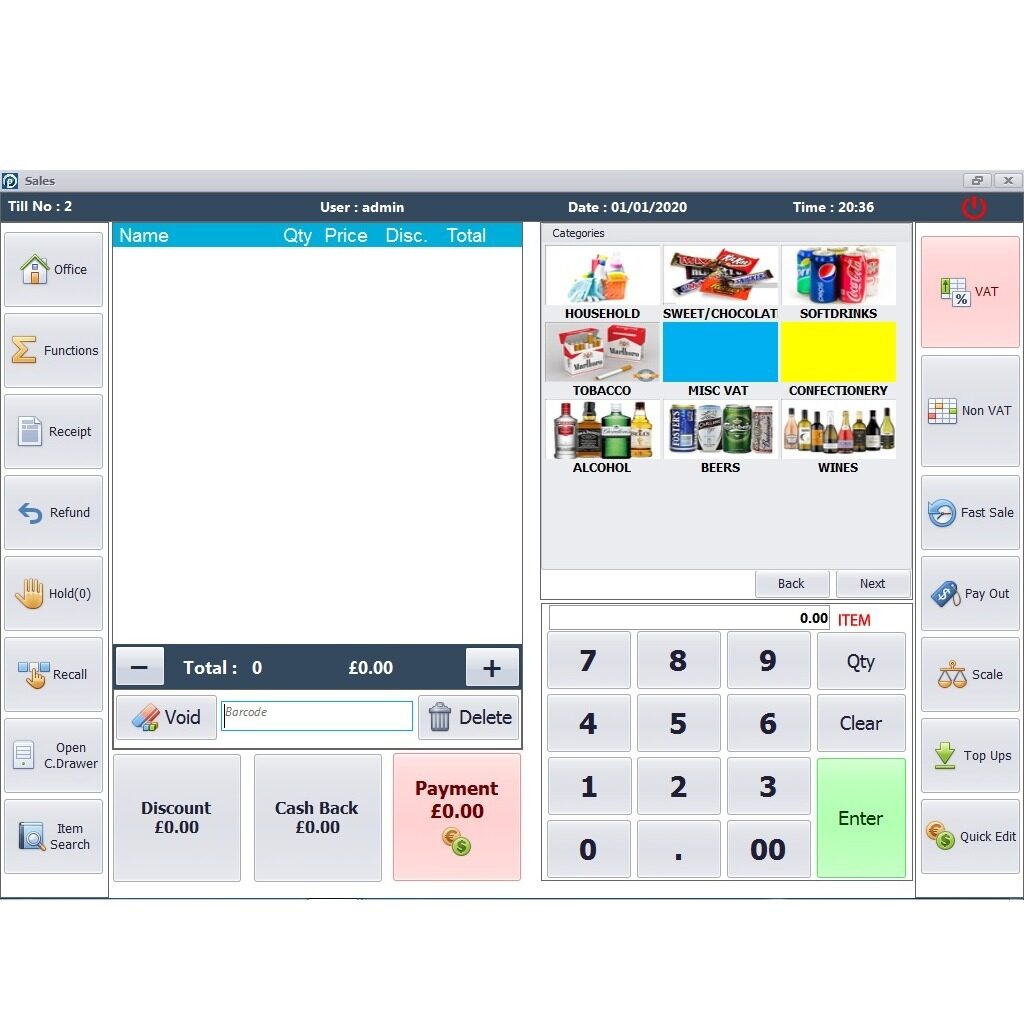
Choosing a POS system is a significant investment, so understanding the costs and potential return is crucial. This section breaks down the financial aspects of implementing POS software, helping you make an informed decision that aligns with your business goals. We’ll cover the various cost components, demonstrate ROI calculation, and provide real-world examples of successful POS implementations.
Cost Components of POS Software
The total cost of ownership for a POS system goes beyond the initial software license fee. Several key components contribute to the overall expense, and understanding each is vital for accurate budgeting.
- Software Licensing Fees: This is the cost of the POS software itself. Pricing models vary widely, from one-time purchases to monthly or annual subscriptions. Factors influencing price include the number of users, features included, and level of support offered.
- Hardware Costs: This includes the purchase or lease of POS terminals, receipt printers, barcode scanners, cash drawers, and potentially other peripherals like customer-facing displays. The cost of hardware can significantly impact the overall budget, especially for businesses with multiple locations or high transaction volumes.
- Implementation and Training Costs: Setting up the POS system often involves professional services for installation, configuration, and data migration. Training staff on how to use the new system is also a significant expense. These costs are often overlooked but can be substantial.
- Ongoing Support and Maintenance Costs: Most POS systems require ongoing support and maintenance, including software updates, technical assistance, and potentially additional training. These costs can be recurring and should be factored into your long-term budget.
Calculating Return on Investment (ROI) for POS Software
Calculating the ROI of your POS system helps determine its financial viability. A simple ROI calculation can illuminate the potential benefits. While specific figures will vary greatly based on your business, a clear understanding of the process is key.
ROI = (Net Profit from POS Implementation – Total Cost of POS Implementation) / Total Cost of POS Implementation
For example, imagine a restaurant experiencing a 15% increase in sales efficiency after implementing a new POS system, resulting in an extra $50,000 in profit annually. If the total cost of the POS system (including hardware, software, and implementation) was $10,000, the ROI would be calculated as follows:
ROI = ($50,000 – $10,000) / $10,000 = 400%
This indicates a strong return on the investment. However, this is a simplified example; a comprehensive ROI calculation should include all relevant costs and benefits.
Case Studies Illustrating Financial Benefits
Several real-world examples highlight the positive financial impact of POS systems. Consider a small retail business that switched to a cloud-based POS system. They experienced a reduction in manual errors, improved inventory management leading to less waste, and streamlined checkout processes resulting in increased customer satisfaction and sales. The improved efficiency and reduced operational costs quickly offset the initial investment.
Another example might involve a restaurant chain that implemented a POS system with integrated online ordering. This resulted in a significant increase in online sales and improved order accuracy. These examples show the diverse ways POS systems can improve profitability.
Cost-Benefit Analysis Template
A structured cost-benefit analysis is essential for comparing different POS solutions. The template below provides a framework for evaluating various options.
| Feature | Solution A | Solution B | Solution C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software Licensing Cost | |||
| Hardware Cost | |||
| Implementation Cost | |||
| Ongoing Support Cost | |||
| Increased Sales | |||
| Reduced Labor Costs | |||
| Improved Inventory Management | |||
| Reduced Errors | |||
| Net Benefit (Revenue – Costs) | |||
| ROI |
This template allows for a side-by-side comparison of different POS solutions, facilitating a data-driven decision. By inputting the relevant costs and benefits for each option, you can easily identify the most financially advantageous choice.
POS Software Security
Protecting your business and your customers’ data is paramount, especially when dealing with sensitive financial information. A secure POS system is not just a good idea; it’s a necessity to maintain customer trust, avoid hefty fines, and prevent significant financial losses. Neglecting security can lead to devastating consequences, ranging from reputational damage to crippling legal repercussions.Data breaches are a significant threat to businesses of all sizes.
Criminals are constantly seeking vulnerabilities to steal credit card numbers, customer personal information, and even business financial data. The impact of a breach extends beyond immediate financial losses; it can damage a business’s reputation and erode customer confidence for years to come.
Data Encryption and Secure Payment Processing
Data encryption is the cornerstone of POS security. This process transforms sensitive data into an unreadable format, making it useless to unauthorized individuals even if it’s intercepted. Strong encryption algorithms, such as AES-256, are essential for protecting data both in transit (between the POS system and the payment processor) and at rest (stored on the system’s hard drive or in the cloud).
Secure payment processing involves adhering to industry standards like PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard), which dictates stringent security requirements for handling credit card information. Failure to comply with PCI DSS can result in significant fines and penalties. Implementing tokenization, a method of replacing sensitive data with non-sensitive substitutes, further enhances security by minimizing the risk associated with storing actual credit card numbers.
Best Practices for Protecting Sensitive Customer Data
Implementing robust security measures is crucial to safeguarding customer data. This includes regular software updates to patch security vulnerabilities, strong password policies for all users, and the use of multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security to user accounts. Access control is also vital; only authorized personnel should have access to sensitive data. Regular security audits and penetration testing can identify and address potential weaknesses before they are exploited by malicious actors.
Employee training is another crucial aspect; educating employees about phishing scams, malware, and other security threats can significantly reduce the risk of internal breaches. Finally, implementing a comprehensive data backup and recovery plan ensures business continuity in the event of a data loss incident.
Security Measures POS Software Vendors Should Implement
POS software vendors bear a significant responsibility for ensuring the security of their products. They should employ secure coding practices to minimize vulnerabilities, regularly update their software to address known security flaws, and conduct rigorous security testing before releasing new versions. Vendors should also offer features such as intrusion detection and prevention systems, real-time monitoring of system activity, and robust logging capabilities to track user actions and identify suspicious behavior.
Transparency in security practices is also crucial; vendors should clearly communicate their security policies and procedures to customers. Furthermore, vendors should offer options for data encryption both in transit and at rest, and ensure compliance with relevant industry standards such as PCI DSS. Finally, proactive measures such as vulnerability scanning and penetration testing should be part of their ongoing development process to identify and mitigate security risks before they can be exploited.
POS Software Scalability
Choosing a POS system that can grow with your business is crucial for long-term success. A system that’s too small will bottleneck your operations as you expand, while one that’s overly complex and expensive from the start might be a burden before you even need its full capacity. Understanding scalability is key to making a smart investment.Scalability in POS systems refers to the system’s ability to handle increasing transaction volumes, data storage needs, and user numbers without significant performance degradation or requiring a complete system overhaul.
This involves considering both hardware and software aspects, ensuring your POS can adapt smoothly to your business’s evolving needs.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise POS Scalability
Cloud-based POS systems generally offer superior scalability compared to on-premise solutions. Cloud providers manage the underlying infrastructure, allowing for easy scaling of resources like processing power and storage simply by adjusting your subscription plan. This eliminates the need for costly hardware upgrades and complex IT management as your business grows. On-premise systems, on the other hand, require significant upfront investment in hardware and ongoing maintenance.
Scaling an on-premise system often involves purchasing and installing new servers, which can be expensive and disruptive. For example, a rapidly growing restaurant chain would find cloud-based POS far easier to manage across multiple locations than attempting to maintain and upgrade on-premise systems at each location.
Factors Influencing POS System Scalability
Several factors determine a POS system’s scalability. These include the system’s architecture (cloud vs. on-premise), the database’s capacity, the software’s ability to handle concurrent users and transactions, and the integration capabilities with other business systems. A robust API is essential for seamless integration with accounting software, inventory management systems, and loyalty programs, allowing for efficient data flow as your business expands.
For instance, a POS system with limited API capabilities might struggle to integrate with a sophisticated inventory management system, hindering the efficient management of a larger inventory. Another critical factor is the vendor’s track record and support. Choosing a reputable vendor with a proven history of scaling solutions for similar businesses will significantly reduce the risk of scalability issues down the line.
Strategies for Scaling a POS System
A well-defined strategy is essential for successfully scaling your POS system. This involves proactive planning, regular system monitoring, and a flexible approach to adapting to changing business needs. Begin by projecting your future transaction volume, user count, and data storage requirements. This allows you to select a POS system with sufficient capacity to meet your anticipated growth. Regularly monitor system performance metrics such as transaction processing speed, database response time, and user experience.
This helps identify potential bottlenecks before they significantly impact operations. Consider adopting a phased approach to scaling, implementing upgrades incrementally rather than undertaking a large-scale overhaul all at once. For example, a small retail store might start with a basic cloud-based system and gradually add features and integrations as needed, rather than investing in a fully-featured, expensive system upfront.
Finally, invest in robust training for your staff to ensure they can effectively utilize the system’s expanded capabilities as it scales.
POS Software Reporting and Analytics
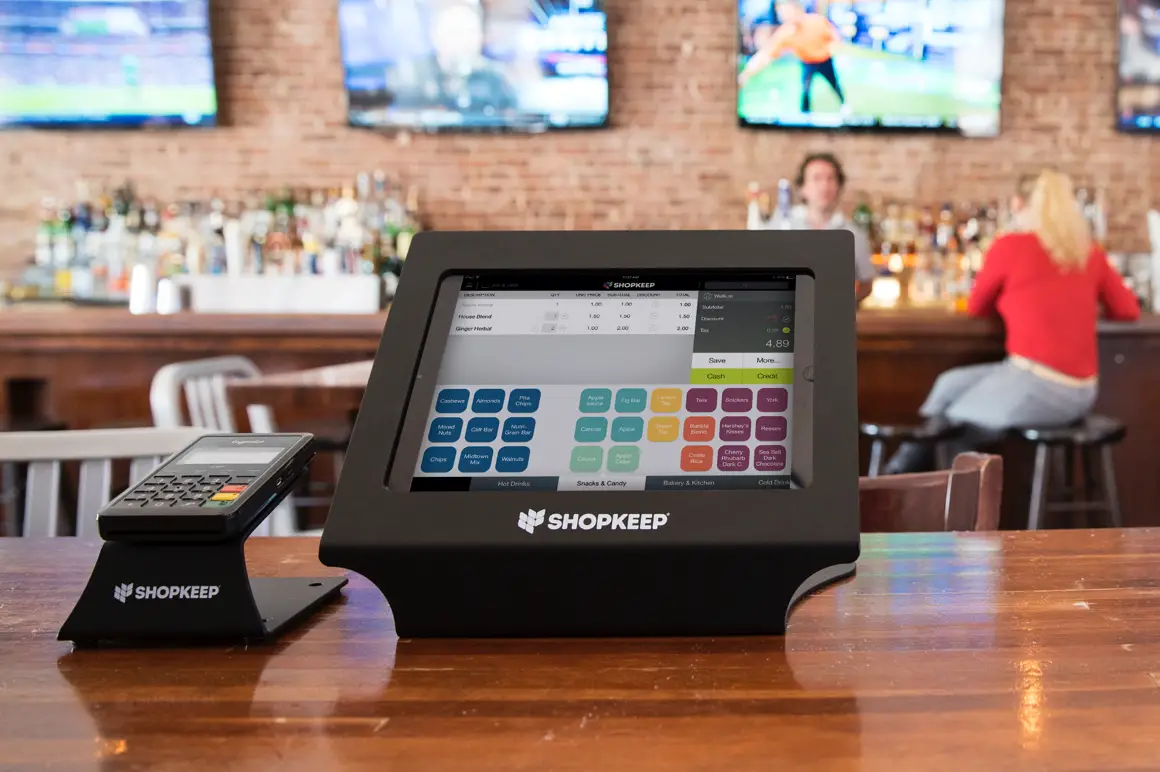

POS systems are more than just cash registers; they’re powerful data generators. Understanding and utilizing the reports they produce is crucial for optimizing your business operations and boosting profitability. Effective analysis of POS data allows you to identify trends, pinpoint areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions to enhance your bottom line.
Types of POS Reports and Their Uses, Pos software
POS software generates a wide array of reports, each offering unique insights into your business. These reports provide a comprehensive overview of sales, inventory, customer behavior, and employee performance. By regularly reviewing these reports, you can gain a clearer picture of your business’s health and identify potential problems before they escalate. For example, sales reports can break down revenue by product, time of day, or employee, revealing best-selling items, peak hours, and top performers.
Inventory reports track stock levels, identifying items that need reordering or those that are slow-moving. Customer reports can segment your customer base based on purchasing habits, allowing for targeted marketing efforts. Employee reports track sales performance and identify areas for training or improvement.
Best Practices for Using POS Data to Improve Business Performance
Leveraging POS data effectively requires a strategic approach. Start by identifying your key performance indicators (KPIs) – the metrics most relevant to your business goals. Regularly analyze your reports to track these KPIs and identify trends. For instance, a consistent decline in sales of a particular item might indicate a need for a price adjustment or a marketing campaign.
Conversely, a surge in sales during a specific time period could suggest the success of a recent promotion. Use this data to inform your decisions, whether it’s adjusting pricing strategies, optimizing staffing levels, or improving marketing campaigns. Don’t just passively review the reports; actively seek patterns and anomalies to understand the “why” behind the numbers.
Creating Custom Reports to Track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Most POS systems offer the ability to create custom reports tailored to your specific needs. This allows you to focus on the metrics most critical to your business. For example, if you’re particularly interested in customer retention, you could create a custom report tracking repeat customer purchases or average order value over time. To create a custom report, you’ll typically need to select the data points you want to include (e.g., sales, date, product, customer), specify the time period, and choose the format for the output (e.g., table, chart).
The exact process will vary depending on your specific POS software, but the underlying principle remains the same: flexibility to track the data that matters most to you.
Essential Metrics to Monitor Using POS Software Analytics
Tracking the right metrics is crucial for effective business management. The following table Artikels some essential metrics you should monitor using your POS software’s analytics capabilities.
| Metric | Description | Calculation | Usefulness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Revenue | Overall sales generated during a specific period. | Sum of all sales transactions | Tracks overall business performance. |
| Average Transaction Value (ATV) | Average amount spent per transaction. | Total Revenue / Number of Transactions | Indicates customer spending habits and effectiveness of upselling/cross-selling. |
| Customer Retention Rate | Percentage of customers who make repeat purchases. | (Returning Customers / Total Customers) – 100 | Measures customer loyalty and effectiveness of retention strategies. |
| Inventory Turnover Rate | How quickly inventory is sold and replaced. | Cost of Goods Sold / Average Inventory | Identifies slow-moving items and potential inventory issues. |
POS Software Customer Support
Running a business relies heavily on your POS system’s smooth operation. Downtime means lost sales and frustrated customers. That’s why having reliable customer support is crucial – it’s your safety net when things go wrong. A responsive support team can mean the difference between a minor hiccup and a major crisis.Choosing a POS system isn’t just about the features; it’s about the ongoing support you’ll receive.
The quality of customer support directly impacts your business efficiency and overall satisfaction. Understanding the different options and asking the right questions is key to making an informed decision.
Customer Support Options Comparison
POS software vendors offer a variety of customer support options, each with its own pros and cons. Some offer basic email support, while others provide comprehensive packages including phone support, live chat, and even dedicated account managers. The level of support you need will depend on your business size, technical expertise, and comfort level with troubleshooting.
- Email Support: Typically the most basic level, email support offers a written record of your interactions but can be slower than other methods.
- Phone Support: Provides immediate assistance and allows for clearer communication, especially for complex issues. However, wait times can vary.
- Live Chat Support: Offers quick answers to simple questions, but may not be suitable for intricate problems requiring detailed explanations.
- Dedicated Account Manager: Provides personalized support and proactive assistance, ideal for larger businesses with complex needs. This is usually a premium service.
- Knowledge Base/Help Center: Many vendors offer online resources like FAQs, tutorials, and troubleshooting guides. This self-service option can resolve many common issues quickly.
Questions to Ask Potential Vendors
Before committing to a POS system, thoroughly investigate the vendor’s customer support capabilities. Asking specific questions will help you determine if their support aligns with your business needs and expectations.
- What are your customer support hours of operation?
- What channels do you offer for customer support (e.g., phone, email, chat, ticketing system)?
- What is your average response time for different support channels?
- Do you offer 24/7 support, or is there an emergency contact available outside of regular business hours?
- What types of training and onboarding support do you provide?
- Do you offer remote support or on-site visits for troubleshooting?
- What is your process for escalating complex issues or bugs?
- What is your customer satisfaction rating or feedback score?
- Can you provide case studies or testimonials from other clients regarding their experiences with your support team?
Characteristics of an Ideal POS Support Team
The ideal POS support team is proactive, knowledgeable, and readily available. They should be able to quickly diagnose and resolve issues, and provide clear and concise solutions. Furthermore, they should be patient and empathetic, understanding that technical difficulties can be frustrating for business owners.
- Responsiveness: Quick response times are essential, especially during critical situations.
- Expertise: Support staff should possess in-depth knowledge of the POS system and related technologies.
- Problem-Solving Skills: The ability to diagnose and resolve issues efficiently is crucial.
- Communication Skills: Clear, concise, and patient communication is vital for effective support.
- Accessibility: Multiple support channels should be available to cater to different preferences.
POS Software Trends and Future Developments
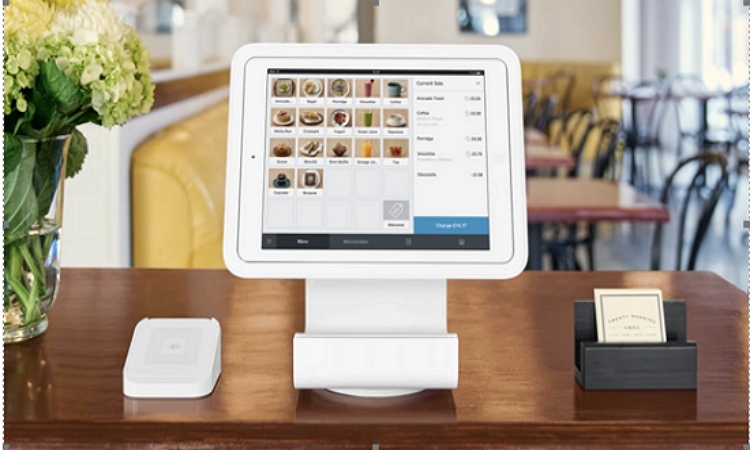

The point-of-sale (POS) system landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer expectations. Understanding these trends is crucial for businesses looking to optimize operations and stay competitive. This section explores key emerging trends, the impact of mobile POS, the role of AI, and predictions for the future of POS software.
Mobile POS Systems and Their Impact on Retail
Mobile POS (mPOS) systems, utilizing smartphones or tablets, have revolutionized retail. The portability and flexibility of mPOS allow businesses to process transactions anywhere, enhancing customer service and expanding sales opportunities. For example, a clothing retailer can now process sales on the floor, avoiding long lines at the traditional checkout counter, improving customer experience and potentially increasing impulse purchases.
This increased convenience extends beyond brick-and-mortar stores; mPOS facilitates seamless transactions at pop-up shops, events, and even curbside pickup locations, significantly expanding a business’s reach and operational flexibility. The reduced infrastructure costs associated with mPOS also make it an attractive option for startups and smaller businesses.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in POS Software
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming POS systems, offering a range of functionalities that enhance efficiency and decision-making. AI-powered features include predictive analytics for inventory management, personalized customer recommendations based on purchase history, and fraud detection through anomaly identification in transaction patterns. For instance, an AI-driven POS system might alert a manager to potential theft based on unusual employee login times or transaction values.
Furthermore, AI can automate tasks such as data entry and reporting, freeing up staff for other crucial activities. The integration of AI allows businesses to gain valuable insights from their data, leading to more effective strategies for sales optimization and customer relationship management.
Emerging Trends in POS Software Technology
Several key trends are shaping the future of POS software. Cloud-based POS systems are becoming increasingly prevalent, offering advantages such as scalability, accessibility, and reduced IT infrastructure costs. The rise of omnichannel retail is driving the need for integrated POS systems that seamlessly connect online and offline sales channels, providing a unified customer experience. Furthermore, the increasing adoption of contactless payment methods, such as Apple Pay and Google Pay, necessitates POS systems equipped to handle these technologies securely and efficiently.
Blockchain technology is also emerging as a potential solution for enhancing security and transparency in transactions.
Predictions for the Future of POS Software and its Applications
Looking ahead, we can anticipate further integration of AI and machine learning to personalize the customer experience and optimize business operations. Expect to see even greater emphasis on data security and compliance with evolving regulations. The convergence of POS systems with other business software, such as CRM and ERP, will become increasingly common, streamlining workflows and providing a holistic view of business performance.
Finally, the continued adoption of cloud-based solutions will lead to more flexible and scalable POS systems, enabling businesses of all sizes to leverage the power of advanced technology. For example, we might see POS systems that automatically adjust pricing based on real-time demand or competitor pricing, leveraging AI and market data analysis.
Outcome Summary
Ultimately, choosing and implementing the right POS software is a game-changer for any business. From optimizing daily operations and boosting efficiency to gaining invaluable insights into your customer base and overall performance, the benefits are undeniable. By carefully considering the factors we’ve discussed – features, cost, security, scalability, and support – you can confidently select a system that perfectly aligns with your business goals.
Don’t just survive – thrive. Embrace the power of POS software.
Key Questions Answered
What’s the difference between cloud-based and on-premise POS systems?
Cloud-based systems are hosted online, accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. On-premise systems are installed directly on your business’s computers and servers. Cloud-based offers flexibility and accessibility, while on-premise provides more control but requires more IT maintenance.
How much does POS software typically cost?
Pricing varies wildly depending on features, vendor, and whether you’re paying monthly or for a one-time license. Expect to pay anywhere from a few hundred dollars annually to several thousand, potentially more for enterprise-level solutions.
What kind of hardware do I need for POS software?
The hardware requirements depend on the specific POS system. You’ll generally need a computer (desktop or tablet), a barcode scanner, a receipt printer, and a payment processing device (card reader). Some systems may also require specialized hardware like a cash drawer or kitchen display system.
Is my data safe with POS software?
Reputable POS vendors prioritize data security with encryption and other safeguards. However, always check the vendor’s security policies and ensure they comply with relevant data protection regulations. Regular software updates are also critical for patching security vulnerabilities.
What if I need help with my POS software after I buy it?
Good POS vendors offer various support options, such as phone support, email support, online help resources, and even dedicated account managers. Before purchasing, investigate the support options available and check customer reviews to gauge the quality of support.
